Hypercholesterolemia
What is Hypercholesterolemia?
It is most commonly, described as increased ranges of low-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (LDL-C) or non-high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (HDL-C); an choice time period is dyslipidemia, which encompasses multiplied triglycerides, low tiers of HDL-C, and qualitative lipid abnormalities.
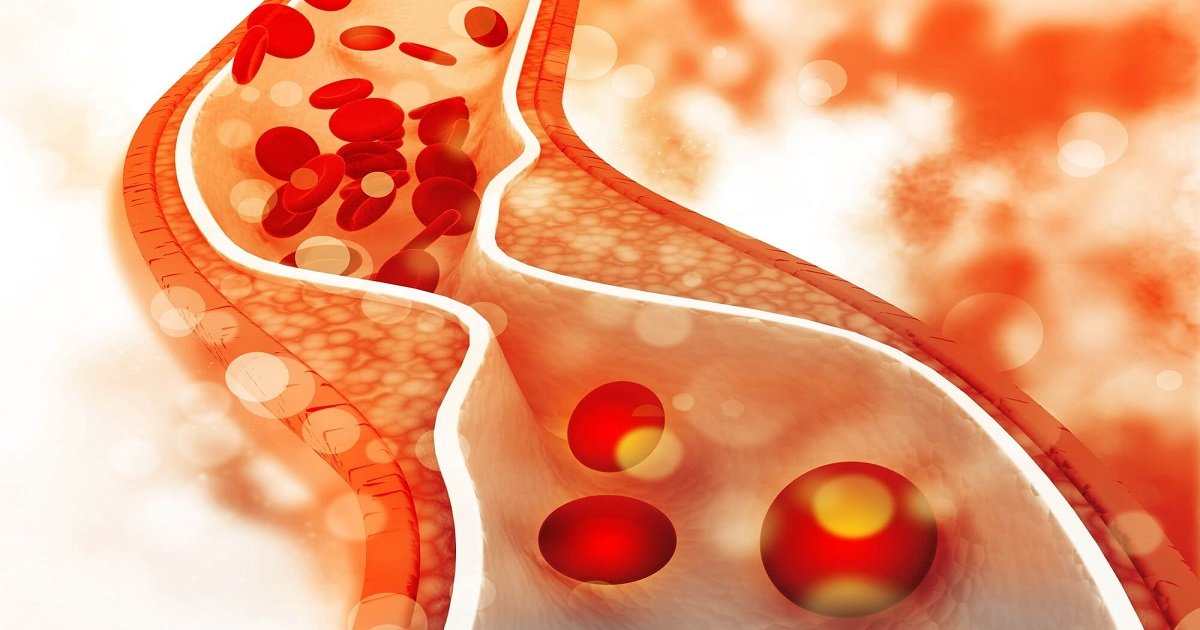
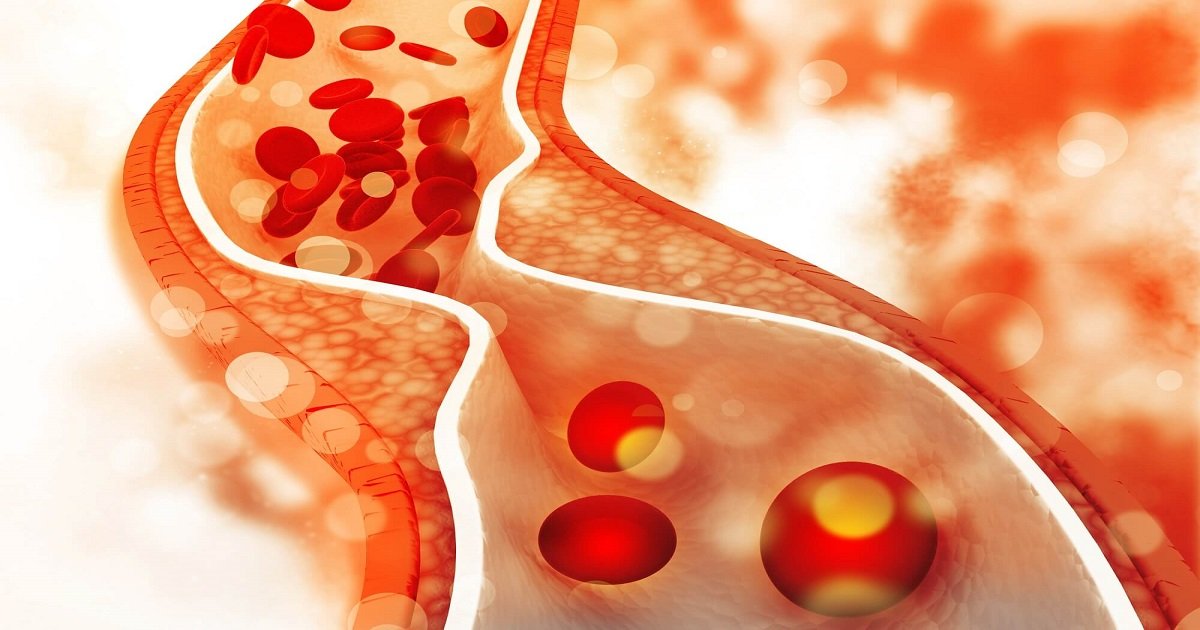
Hypercholesterolemia is an necessary danger issue for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, such as cerebrovascular disease, coronary coronary heart disease, and peripheral arterial disease; it is typically symptomatically quiescent till massive atherosclerosis has developed.
Complications of hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis encompass:
- myocardial infarction
- ischemic cardiomyopathy
- unexpected cardiac death
- ischemic stroke
- erectile dysfunction
- claudication
- acute limb ischemia.
Risk elements for secondary hypercholesterolemia in industrialized populations consist of a sedentary way of life and a weight loss plan characterised by using the immoderate consumption of saturated fats, trans-fatty acids, and cholesterol.
Other associations encompass:
- diabetes,
- extra physique weight usually in the belly region,
- hypothyroidism
- nephrotic syndrome
- cholestatic liver disease
Low HDL-C stages are related with smoking and stomach obesity.
It is recognized by way of a lipid profile, consisting of measurements of complete cholesterol, LDL-C (estimated or direct), HDL-C, and triglycerides. Non-HDL-C is calculated by using the subtraction of HDL-C from whole cholesterol.
Hypercholesterolemia is handled with way of life changes such as:
dietary changes
exercise,
smoking cessation
as nicely as pharmacologic intervention with statin therapy, and selective use of the ldl cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe (which are found in our product Downsterolin®)
Finally Hypercholesterolemia definition is:
Hypercholesterolemia, an elevation of whole ldl cholesterol (TC) and/or low-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (LDL-C) or non-high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (HDL-C) (defined as the subtraction of HDL-C from TC) in the blood, is additionally regularly referred to as dyslipidemia, to embody the reality that it would possibly be accompanied via a limit in HDL-C, an make bigger in triglycerides, or qualitative lipid abnormalities.
Dyslipidemia is labeled as serum TC, LDL-C, triglycerides, apolipoprotein B, or lipoprotein(a) concentrations above the ninetieth percentile, or HDL-C or apolipoprotein A-I concentrations under the tenth percentile for the widely wide-spread population.
However, these basic percentile cut-off factors have to now not be used too rigidly in defining dyslipidemia.
For example, proof suggests that lipoprotein(a) ≥80th percentile is atypical and linked to accelerated cardiovascular risk.

 info@utopiapharma.com
info@utopiapharma.com
 Plot No. (2) Industrial Zone (A7) - formerly Zizinia - Cairo - Ismailia Road - 10th of Ramadan - Sharkia
Plot No. (2) Industrial Zone (A7) - formerly Zizinia - Cairo - Ismailia Road - 10th of Ramadan - Sharkia